An initial coin offering (ICO) is the equivalent of an initial public offer (IPO). An ICO is a method for companies to raise money to create a new currency, app, or service.
What is an Initial Coin Offering (ICO), and how does it work?
Investors interested in investing can purchase an initial coin offer to receive a new cryptocurrency token from the company. The token could be used to purchase a product or service, or simply a stake in the company.
Key Takeaways:
-
Initial coin offerings (ICOs) are a popular way of raising funds for products or services that are often related to cryptocurrency.
-
ICOs can be compared to initial public offerings. However, coins issued in an ICO may also have utility for a product or service.
-
Some ICOs have provided huge returns for investors. Many others have failed to perform or turned out fraudulent.
-
An ICO requires that you first buy a digital currency. You also need to have a basic understanding of cryptocurrency exchanges and wallets.
-
ICOs are unregulated most of the time, so investors should exercise caution when researching and investing in ICOs.
How an Initial Coin Offering is (ICO) Made?
A cryptocurrency is a digital currency. If a project is looking to raise funds through ICO, its first step should be to decide how to structure it. There are many ways to structure ICOs, including:
- The static supply and price: A company can establish a funding goal or limit. This means that each token sold during an ICO will have a fixed price and total supply.
- Dynamic price and static supply: An ICO may have a static supply and a funding goal. This means that the total price per token will be determined by the amount of funds received.
- Static price and dynamic supply: Some ICOs have a static price but a dynamic supply. This means that the amount of funding received will determine the supply.
Below are three examples of ICOs.
The crypto project creates a whitepaper to help potential investors understand the ICO. To explain the ICO, the promoters of the project use the whitepaper.
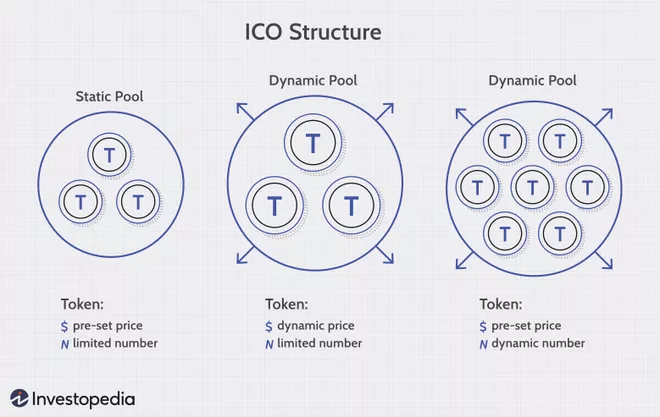
Image by Sabrina Jiang © Investopedia 2020
- What the project is all about?
- The project should fulfill the following needs
- What amount of money is required for the project?
- How many virtual tokens will founders keep?
- Which type of payment (and which currencies) is accepted?
- How long will the ICO campaign last?
As part of its ICO campaign, the whitepaper is released by the project. It aims to encourage supporters and enthusiasts to buy tokens. To buy the tokens investors can use fiat or digital currency. It’s becoming more common for investors to pay with other cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin and Ethereum. These tokens can be used in the same way as stock shares that were sold during an IPO.
All money received in an ICO may be returned to investors if it is less than the minimum amount specified by the ICO’s criteria. If the ICO is unsuccessful, it will be canceled. If all funding requirements are met within the timeframe, the money is used to pursue the project’s goals.
Who can launch an ICO?
An ICO can be launched by anyone. Anyone who has the right tech can launch a new cryptocurrency. There is very little regulation in the U.S.
This lack of regulation means that anyone can pretend to have a legitimate ICO and then disappear with the money. An ICO is one of the easiest to scam out of all funding options.
Do your research before you decide to invest in a new ICO. First, ensure that the people behind the ICO are trustworthy. It is important to check the history of the product’s lead with crypto or Blockchain. It’s a red flag if the project does not involve someone with relevant, easily verified experiences.
Famous actors and entertainers such as Steven Seagal sometimes urge their fans to invest in a new ICO. At the end of 2017, Centra Tech raised $30 million. Centra Tech was eventually deemed a fraud by the U.S. regulators. The two celebrities and three Centra Tech founders pleaded guilty to ICO fraud.
Although anyone can launch an ICO and establish a business, it doesn’t necessarily mean everyone should. Consider whether your company would benefit significantly from an initial coin offering if you’re thinking of organizing one.
Take Note
ICO activity has declined dramatically since 2019, partly because of the legal grey area in which ICOs operate. Websites like TopICOlist.com can be used to compare different ICOs.
ICOs are a hot topic. There are many sites where investors can meet to discuss potential opportunities. Before investing in ICOs, investors should familiarize themselves with the cryptocurrency industry and learn about each ICO. Potential investors need to exercise extreme caution when investing in ICOs, as they are not well-regulated.
When investing in an ICO, there is no guarantee that investors won’t fall for a scam. To help avoid ICO scams, you can:
- It is important that project developers clearly communicate their goals. Successful ICOs have clear, simple white papers that are easy to understand and contain concise goals.
- Transparency is key. An ICO company should provide transparency to investors.
- Check out the ICO’s terms and conditions. Traditional regulators do not usually oversee this space so it is the responsibility of investors to ensure an ICO’s legitimacy.
- Make sure that ICO funds are in an escrow wallet. This wallet is protected against fraud by requiring multiple access keys.
You will typically need another cryptocurrency in order to invest in an ICO. New tokens can only be bought using an existing cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin. ICO investors must have at least two cryptocurrency wallets.
- One crypto wallet can store another cryptocurrency, such as Bitcoin or Ethereum
- A second cryptocurrency wallet is required to store the currency or token being sold in the ICO.
Initial Coin Offering (ICO) vs. Initial Public Offering (IPO).
Initial public offerings of stock are a way for companies to raise capital. They allow them to distribute shares of their stock to investors. Token sales or coins are used to raise funds for crypto companies. Both investors are bullish on the company and cryptocurrency and will invest in the belief that the asset’s price will rise over time.
An ICO is not the same as an initial public offering stock. This is because investing in an ICO does not give you ownership of the crypto company or project. Participants in ICOs are betting that a currency currently worthless will eventually rise in value beyond its initial purchase price.
IPOs are heavily regulated by government agencies such as the Securities and Exchange Commission. 6 The decentralized nature and lack of regulation of crypto projects mean that ICO structures can be very different. Contrary to this, most IPOs have a similar structure.
IPOs are generally funded by more conservative investors who expect a return on their investment. However, ICOs can be funded by risk-tolerant supporters who are eager to invest in a new and exciting project. An ICO is different from a crowdfunding event in that it can provide financial gains over time. Crowdfunding initiatives essentially only receive donations. Crowdsales is another name for ICOs. This is because they offer the possibility of financial gains.
Advantages and disadvantages of Initial Coin Offerings
Online services make it easy to generate cryptocurrency tokens. This makes it extremely simple for companies to think about launching an ICO. ICO managers create tokens in accordance with the terms of an ICO. They then receive the tokens and distribute them to investors. ICOs are not regulated like the SEC so funds lost due to fraud and incompetence might never be recovered.
ICO investors are often motivated by the belief that tokens will rise in value following the launch of cryptocurrency. An ICO offers the opportunity for high returns.
However, the legality and safety of digital assets or cryptocurrency are not certain to be maintained. But the legality of cryptocurrency or digital assets is not guaranteed to last.
SEC introduces the HoweyCoin
In 2018, the SEC introduced a fake currency called HoweyCoin in order to warn individual investors about the dangers of ICOs. In 2018, the SEC introduced a fake coin called the
On December 11, 2017, the SEC stopped an ICO being conducted by Munchee, a California-based company that offers a food review app. This was the first time the SEC has cracked down on ICOs. Munchee wanted to raise funds to create a cryptocurrency to be used in the app to order food. The SEC issued a cease and desist letter to Munchee, describing the ICO as an offer of unregistered securities.
Examples of Initial Coin Offerings
The 2014 Ethereum ICO is a prominent example of an initial coin offer. The Ethereum ICO raised $18 Million in 42 days. In 2015 Antshares launched a two-phase ICO. Later, Neo was rebranded as Antshares. This ICO’s first phase ended in October 2015. The second phase continued until September 2016. Neo generated approximately $4.5 million during this ICO’s first phase. The second phase continued until September 2016.
Another example is that Dragon Coin raised approximately $320 million during a one-month ICO in March 2018. In 2018, the EOS platform company broke Dragon Coin’s record of raising $4 billion in a year-long ICO.
Sometimes, ICOs that offer remarkable returns on investments don’t always raise the most money.
Investing in cryptocurrencies, Initial Coin Offerings (“ICOs”), and other Initial Coin Offerings (“ICOs”) can be risky and speculative. This article does not recommend that you invest in cryptocurrencies. Every person’s financial situation is different. A qualified professional should be consulted before making any financial decision. Investopedia does not make any representations or warranties regarding the accuracy or timeliness of the information.