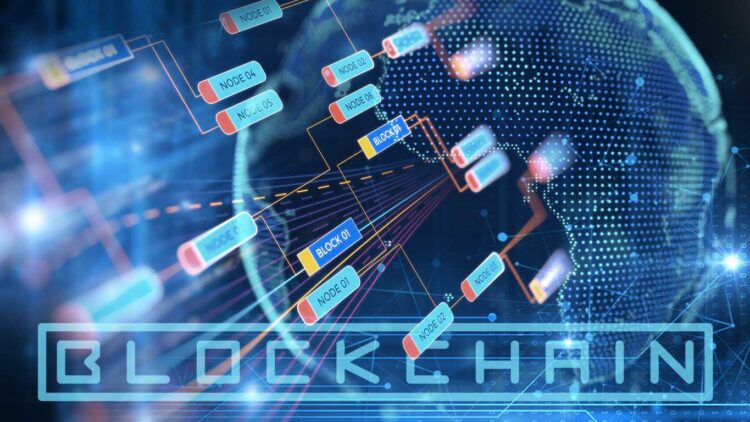
Blockchain defined in simple words:
Blockchain appears to be convoluted, and it certainly can be. However, its fundamental idea is very straightforward. A blockchain acts as a repository or, in simpler words, a ‘database.’
A database is simply an assortment of stored data electronically on a system. Filtering and locating for data or information in such an environment is efficient. Since a tabular configuration is applied to arrange data in a database. Large-scale databases cater to significantly extensive quantities of data through powerful serves. This data can be accessed by multiple users at the same time.
Blockchain as database stores transferable or transactional records as a ‘block electronically.’ Several databases contain Blocks of the public, which form the ‘chain’ in a network linked by peer-to-peer nodes. Generally, a Blockchain is referred to as a ‘digital ledger.’
Working of Blockchain

Image Credits: healthcareitnews.com
Since a Blockchain is a digital ledger, a block is made when users execute a Blockchain platform transaction. This block signifies that the transaction has been created.
After which, the requested transaction is broadcasted over the peer-to-peer network, made of nodes (powerful computers), subsequently validating the block.
In the next step, the transaction is confirmed and approved. It is integrated with other blocks to generate a new block of data for the ledger. Note: The owner’s digital signature supports every transaction in this ledger. This is done to verify the trade’s validity and defends any unlikely interference.
It is imperative to note that a more protected block is built and bound to the other based on cryptographic fundamentals with every new transaction. Therefore, the data in the digital ledger is profoundly secure.
Where is Blockchain used?
A blockchain is a reliable tool with numerous applications that can be utilized by industries, businesses, and the general public.

Image Credits: theneweconomy.com
While cryptocurrency mining transactions remain the most cited example for Blockchain, it has a relatively wide range of use. For instance, in the finance industry, it can track fraudulent exchanges. Transfer of intellectual properties between businesses or artists, or even communicating a patient’s medical records can be sent on a highly secure and efficient platform.

Image Credits: environmentalleader.com
In another simple example, IBM has created the “IBM Food Trust – Blockchain for the world’s food supply.” There have been several outbreaks of salmonella or e Coli in the food industry; even unsafe materials were involuntarily exposed to food products. Locating the exact point and reach of these was an extensively tedious task of weeks, endangering the lives of those who have or may consume the product.
This trust’s main objective is to trail food products across the supply ecosystem of food producers, suppliers, retailers till its delivery. Any contaminated product found will be traced to its origin.
Even locating all points where it would have been exposing to the problem. Therefore, making it simpler to identify its reach and potentially save lives.
Companies that have integrated Blockchain Technology include Walmart, Pfizer, Unilever, AIG, Siemens, and many others.
Highlights of utilizing Blockchain
Highly Security and Availability

Image Credits: allerin.com
Blockchain utilizes digital signatures to maintain an impenetrably secure environment, making it challenging to ruin or manipulate the data without the user’s approval. Thus, it provides integrity through unique cryptographic algorithms without third-party interference and makes it immutable and exceptionally accurate.
In contrast to centralized systems, Blockchain is a decentralized arrangement of P2P Networks. In this manner, regardless of whether one user goes down, the other users will still function. Hence, it is exceptionally accessible because of its decentralized nature.
Decentralization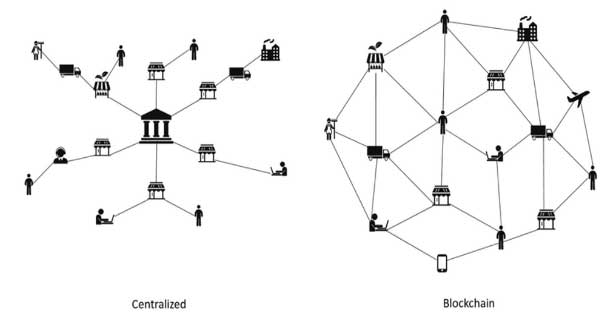
Image Credits: researchgate.net
In terms of authority: Traditionally, a user requires the permission of administrative or regulatory authority for transactional exchanges. But with Blockchain, the business is done more efficiently through common consensus, without a third party.
In terms of systems: Blockchain is not confined to a central database. Somewhat, it is duplicated and spread across a network, making it hard to manipulate. If accidentally this duplicate of the blockchain lands in the hands of an uninvited user, only a single copy would be compromised, instead of the whole network.
Transparency and Efficiency
Image Credits: medium.com
In contrast to centralized systems, Blockchain performs by absolute transparency. Organizations that utilize Blockchain technology have decentralized networks, eliminating the need for a centrally-controlled authority. Hence, enhancing a more transparent system.
While executing transactions through a centralized institution like a Bank confines users to working hours or time-zones. To our advantage, Blockchain is available 24 hours a day, seven days a week, and 365 days a year. While with its aid, a transaction can take a few minutes. It even eliminates additional administration fees.
Limitations of Blockchain
Lack of Regulation
Image Credits: investopedia.com
Although the blockchain networks preserve privacy and are highly secure from uninvited hackers, since there is no regulatory authority to police illegal trading, Silk Road is an online black-market and part of the ‘dark web.’ The platform carried out illicit exchanges from 2011 till 2013 when the FBI shut it down. On this website, illegal purchases were made in cryptocurrencies without tracing them.
Cost of Technology
Image Credits: thegaurdian.com
Despite saving administration fees, the technology used is quite expensive. For instance, the cost of bitcoin mining, such as the electricity bills, should be lesser than what the user earns through mining bitcoins to ascertain a profit.
But usually, users pursue to drive up their electricity bills to justify profitable transactions on the Blockchain. But at the same time, when a miner adds a block to the bitcoin blockchain, he is compensated with enough bitcoin to make his and energy advantageous.
How is Blockchain different from Cloud Computing?
Often people assume cloud computing and Blockchain to be one of the same. Well, it is not so. Here are some significant points of differentiation:
- Blockchain technologies use encrypted systems to provide ledger databases. While cloud computing centers on-demand computing services, notably for data storage.
- Blockchains function on cryptographical fundamentals and assure security against data tempering because it does not rely on any third-party authority. In the cloud, data security isn’t assurable since the main objective is to enable multiple user access.
- Blockchains are modern technologies, they do not provide services. On the other hand, cloud computing is a computing tool that provides services. Namely: Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS).
- Records in Blockchains are immutable, whereas data residing in the cloud are mutable.
- For instance, companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS), IBM, Google, and Microsoft provide cloud computing services. Whereas Ethereum, Quorum, and Bitcoin utilize blockchain technology.
Based on its current expanded use, it appears to be that Blockchain is ready to govern the advanced digital universe of the not-so-distant future. Subsequently, a well-evolved form of this technology can impact and enhance, economies of the world. Advanced Blockchains will solve and influence, store, and exchange data for every industry.